
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Optimal Coefficient of Variance Threshold to Minimize Hypoglycemia Risk in Individuals with Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Received March 14, 2023 Accepted August 12, 2023 Published online March 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0083 [Epub ahead of print]

- 510 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the optimal coefficient of variance (%CV) for preventing hypoglycemia based on real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) data in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) already achieving their mean glucose (MG) target.
Methods
Data from 172 subjects who underwent rt-CGM for at least 90 days and for whom 439 90-day glycemic profiles were available were analyzed. Receiver operator characteristic analysis was conducted to determine the cut-off value of %CV to achieve time below range (%TBR)<54 mg/dL <1 and =0.
Results
Overall mean glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.8% and median %TBR<54 mg/dL was 0.2%. MG was significantly higher and %CV significantly lower in profiles achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 compared to %TBR<54 mg/dL ≥1 (all P<0.001). The cut-off value of %CV for achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 was 37.5%, 37.3%, and 31.0%, in the whole population, MG >135 mg/dL, and ≤135 mg/dL, respectively. The cut-off value for %TBR<54 mg/dL=0% was 29.2% in MG ≤135 mg/dL. In profiles with MG ≤135 mg/dL, 94.2% of profiles with a %CV <31 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL <1, and 97.3% with a %CV <29.2 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/ dL=0%. When MG was >135 mg/dL, 99.4% of profiles with a %CV <37.3 achieved %TBR<54 mg/dL <1.
Conclusion
In well-controlled T1DM with MG ≤135 mg/dL, we suggest a %CV <31% to achieve the %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 target. Furthermore, we suggest a %CV <29.2% to achieve the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL =0 for people at high risk of hypoglycemia.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
- You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):122-133. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0431
- 1,088 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
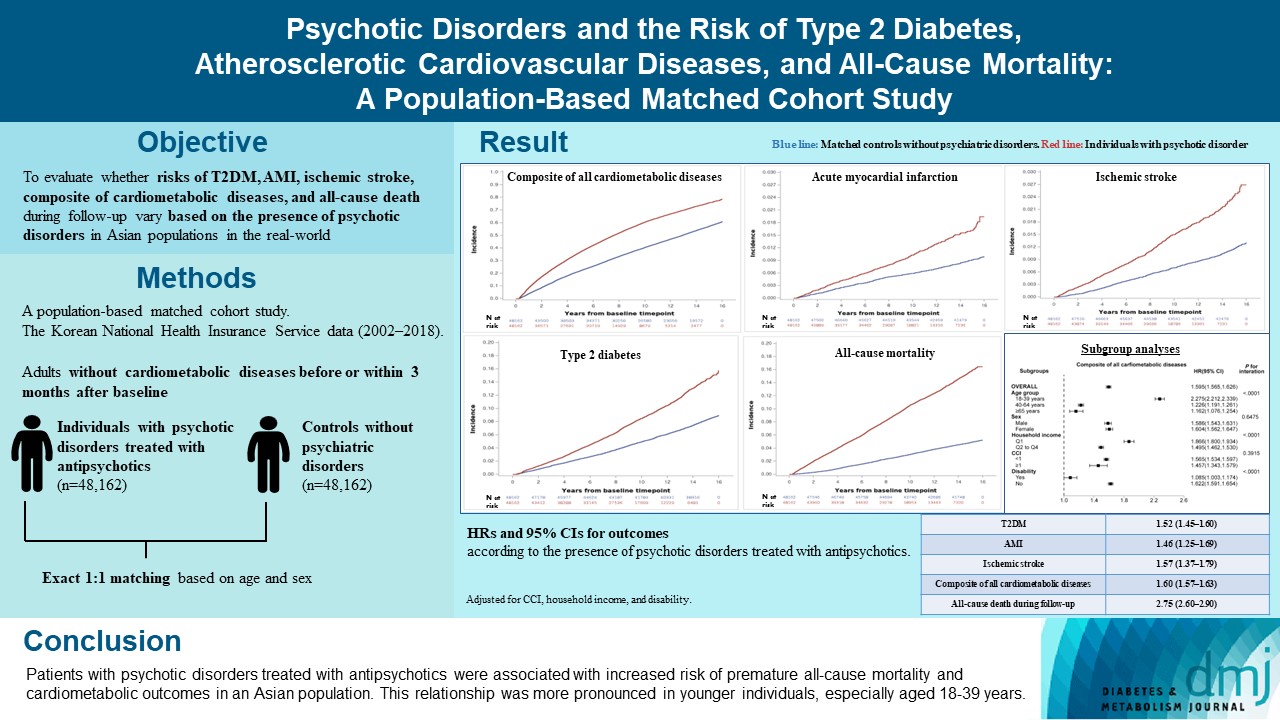
The effects of psychotic disorders on cardiometabolic diseases and premature death need to be determined in Asian populations.
Methods
In this population-based matched cohort study, the Korean National Health Insurance Service database (2002 to 2018) was used. The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic stroke, composite of all cardiometabolic diseases, and all-cause death during follow-up was compared between individuals with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics (n=48,162) and 1:1 matched controls without psychiatric disorders among adults without cardiometabolic diseases before or within 3 months after baseline.
Results
In this cohort, 53,683 composite cases of all cardiometabolic diseases (during median 7.38 years), 899 AMI, and 1,216 ischemic stroke cases (during median 14.14 years), 7,686 T2DM cases (during median 13.26 years), and 7,092 deaths (during median 14.23 years) occurred. The risk of all outcomes was higher in subjects with psychotic disorders than matched controls (adjusted hazard ratios [95% confidence intervals]: 1.522 [1.446 to 1.602] for T2DM; 1.455 [1.251 to 1.693] for AMI; 1.568 [1.373 to 1.790] for ischemic stroke; 1.595 [1.565 to 1.626] for composite of all cardiometabolic diseases; and 2.747 [2.599 to 2.904] for all-cause mortality) during follow-up. Similar patterns of associations were maintained in subgroup analyses but more prominent in younger individuals (P for interaction <0.0001) when categorized as those aged 18–39, 40–64, or ≥65 years.
Conclusion
Patients with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics were associated with increased risk of premature allcause mortality and cardiometabolic outcomes in an Asian population. This relationship was more pronounced in younger individuals, especially aged 18 to 39 years.
- Complications
- Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
- So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):290-301. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0299
- 882 View
- 129 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
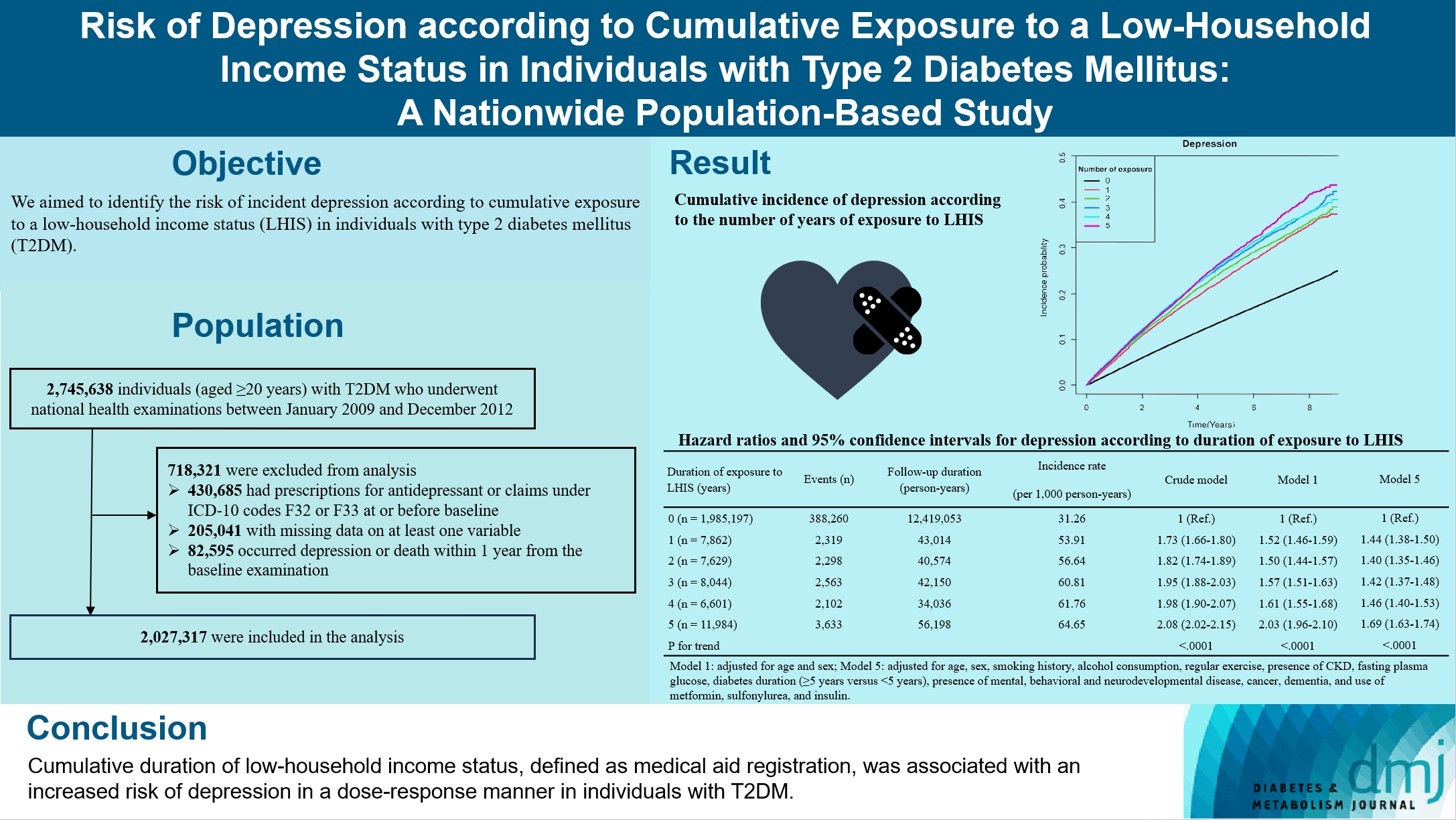
We aimed to identify the risk of incident depression according to cumulative exposure to a low-household income status in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
For this retrospective longitudinal population-based cohort study, we used Korean National Health Insurance Service data from 2002 to 2018. Risk of depression was assessed according to cumulative exposure to low-household income status (defined as Medical Aid registration) during the previous 5 years among adults (aged ≥20 years) with T2DM and without baseline depression who underwent health examinations from 2009 to 2012 (n=2,027,317).
Results
During an average 6.23 years of follow-up, 401,175 incident depression cases occurred. Advance in cumulative number of years registered for medical aid during the previous 5 years from baseline was associated with an increased risk of depression in a dose-dependent manner (hazard ratio [HR], 1.44 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.38 to 1.50]; HR, 1.40 [95% CI, 1.35 to 1.46]; HR, 1.42, [95% CI, 1.37 to 1.48]; HR, 1.46, [95% CI, 1.40 to 1.53]; HR, 1.69, [95% CI, 1.63 to 1.74] in groups with 1 to 5 exposed years, respectively). Insulin users exposed for 5 years to a low-household income state had the highest risk of depression among groups categorized by insulin use and duration of low-household income status.
Conclusion
Cumulative duration of low-household income status, defined as medical aid registration, was associated with an increased risk of depression in a dose-response manner in individuals with T2DM.
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae Jin Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Jung Hae Ko, Nam Hoon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Jeeyun Ahn, Tae Jung Oh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Eugene Han, Sang-Man Jin, Won Suk Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):575-594. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0282
- 5,014 View
- 628 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In May 2023, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association published the revised clinical practice guidelines for Korean adults with diabetes and prediabetes. We incorporated the latest clinical research findings through a comprehensive systematic literature review and applied them in a manner suitable for the Korean population. These guidelines are designed for all healthcare providers nationwide, including physicians, diabetes experts, and certified diabetes educators who manage patients with diabetes or individuals at risk of developing diabetes. Based on recent changes in international guidelines and the results of a Korean epidemiological study, the recommended age for diabetes screening has been lowered. In collaboration with the relevant Korean medical societies, recently revised guidelines for managing hypertension and dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes have been incorporated into this guideline. An abridgment containing practical information on patient education and systematic management in the clinic was published separately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Letter by In-Kyung Jeong Regarding Article, Trends in Prevalence of Hypertriglyceridemia and Related Factors in Korean Adults: A Serial Cross-Sectional Study
In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 80. CrossRef - Association between cardiovascular disease risk and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in individuals with prediabetes: A retrospective cohort study
Myung Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111125. CrossRef - Korea Hypertension Fact Sheet 2023: analysis of nationwide population-based data with a particular focus on hypertension in special populations
Hyeon Chang Kim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Dasom Son, Minsung Cho, Sojung Shin, Yeeun Seo, Eun-Jin kim, Song Vogue Ahn, Sun Ha Jee, Sungha Park, Hae-Young Lee, Min Ho Shin, Sang-Hyun Ihm, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ku Park, Il Suh, Tae-Yong Lee
Clinical Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - A self-powered and supercapacitive microneedle continuous glucose monitoring system with a wide range of glucose detection capabilities
Hye-Jun Kil, Jang Hyeon Kim, Kanghae Lee, Tae-Uk Kang, Ju-Hyun Yoo, Yong-ho Lee, Jin-Woo Park
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2024; 257: 116297. CrossRef - Cardiorenal outcomes and mortality after sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor initiation in type 2 diabetes patients with percutaneous coronary intervention history
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, BongSeong Kim, Mee Kyung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Recommendations for Pharmacological Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Junghyun Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 127. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - A 33-Year-Old Man Presented with Abdominal Pain and Vomiting Starting a Day Ago
Jong Han Choi
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(6): 289. CrossRef - Comorbidity Patterns and Management in Inpatients with Endocrine Diseases by Age Groups in South Korea: Nationwide Data
Sung-Soo Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 14(1): 42. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Low Household Income Status and Death from Pneumonia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, So Hee Park, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):682-692. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0184
- 1,584 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
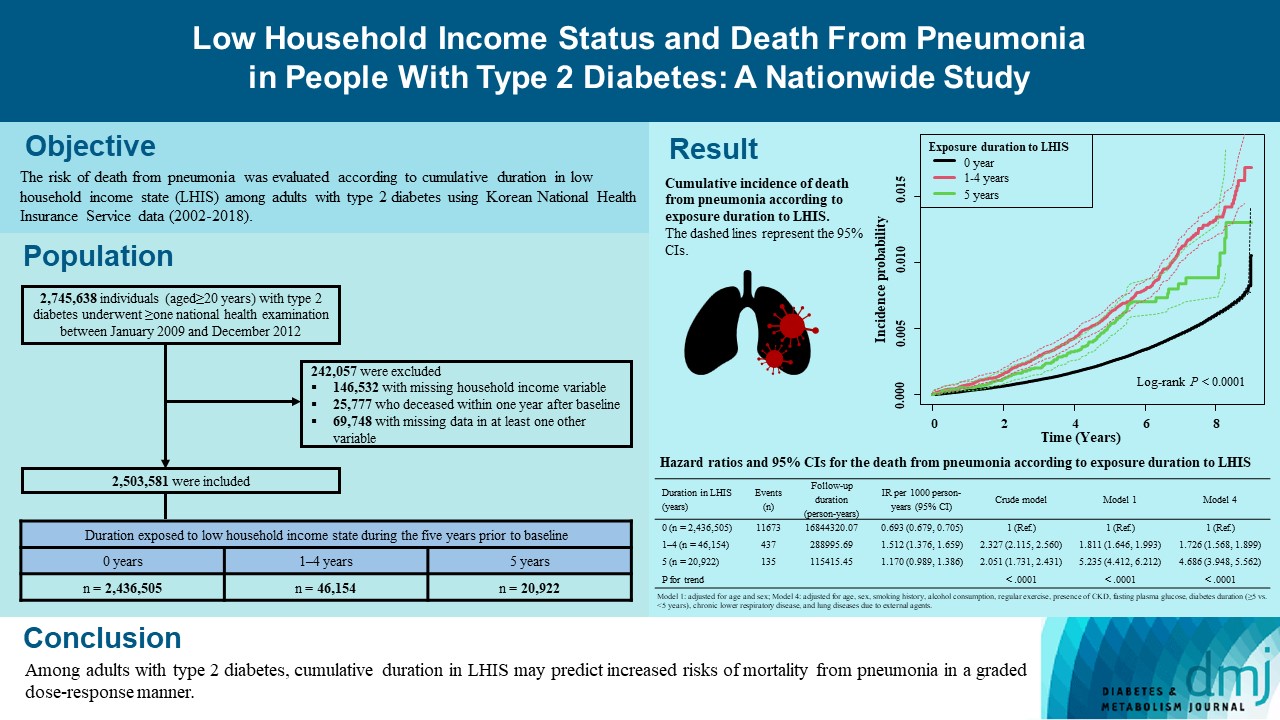
We explored the risk of death from pneumonia according to cumulative duration in low household income state (LHIS) among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Using Korean National Health Insurance Service data (2002 to 2018), the hazards of mortality from pneumonia were analyzed according to duration in LHIS (being registered to Medical Aid) during the 5 years before baseline (0, 1–4, and 5 years) among adults with T2DM who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 (n=2,503,581). Hazards of outcomes were also compared in six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Results
During a median 7.18 years, 12,245 deaths from pneumonia occurred. Individuals who had been exposed to LHIS had higher hazards of death from pneumonia in a dose-response manner (hazard ratio [HR], 1.726; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.568 to 1.899 and HR, 4.686; 95% CI, 3.948 to 5.562 in those exposed for 1–4 and 5 years, respectively) compared to the non-exposed reference. Insulin users exposed for 5 years to LHIS exhibited the highest outcome hazard among six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Conclusion
Among adults with T2DM, cumulative duration in LHIS may predict increased risks of mortality from pneumonia in a graded dose-response manner. Insulin users with the longest duration in LHIS might be the group most vulnerable to death from pneumonia among adults with T2DM.
- Technology/Device
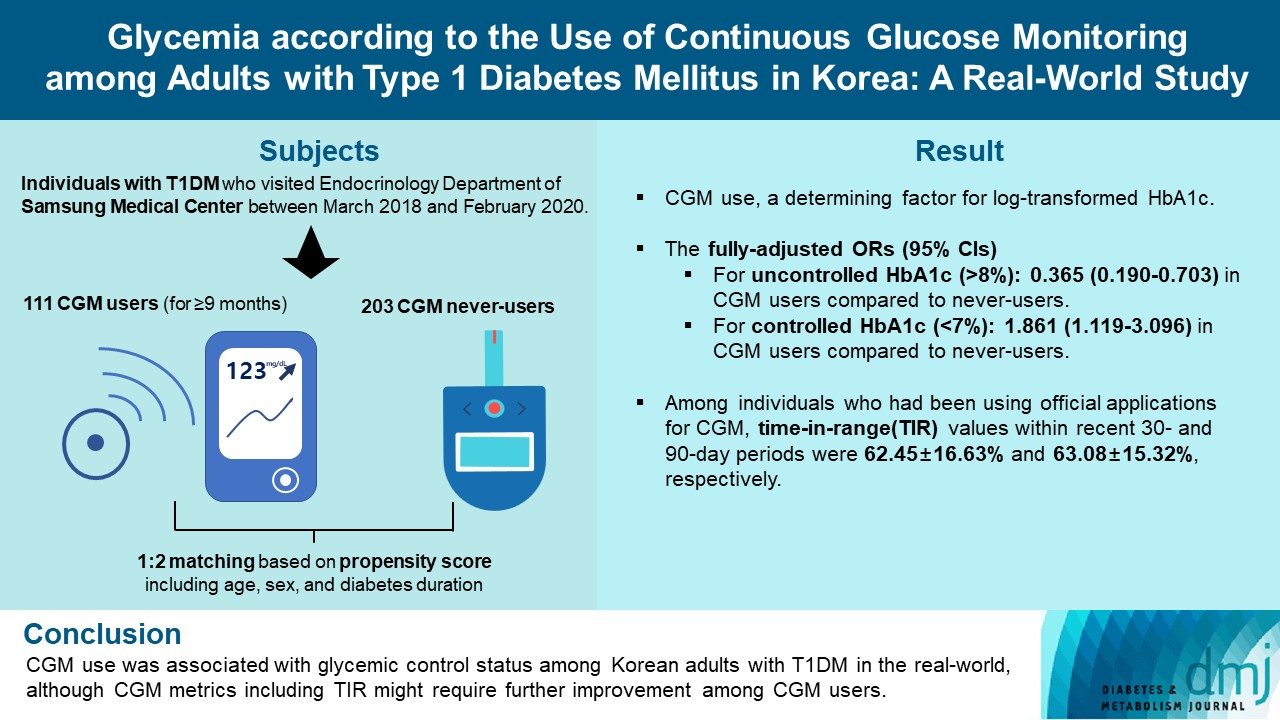
- Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minjee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):405-414. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0032
- 3,252 View
- 122 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We explored the association between continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use and glycemia among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and determined the status of CGM metrics among adults with T1DM using CGM in the real-world.
Methods
For this propensity-matched cross-sectional study, individuals with T1DM who visited the outpatient clinic of the Endocrinology Department of Samsung Medical Center between March 2018 and February 2020 were screened. Among them, 111 CGM users (for ≥9 months) were matched based on propensity score considering age, sex, and diabetes duration in a 1:2 ratio with 203 CGM never-users. The association between CGM use and glycemic measures was explored. In a subpopulation of CGM users who had been using official applications (not “do-it-yourself” software) such that Ambulatory Glucose Profile data for ≥1 month were available (n=87), standardized CGM metrics were summarized.
Results
Linear regression analyses identified CGM use as a determining factor for log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin. The fully-adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) were 0.365 (95% CI, 0.190 to 0.703) in CGM users compared to never-users. The fully-adjusted OR for controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) was 1.861 (95% CI, 1.119 to 3.096) in CGM users compared to never-users. Among individuals who had been using official applications for CGM, time in range (TIR) values within recent 30- and 90-day periods were 62.45%±16.63% and 63.08%±15.32%, respectively.
Conclusion
CGM use was associated with glycemic control status among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world, although CGM metrics including TIR might require further improvement among CGM users. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
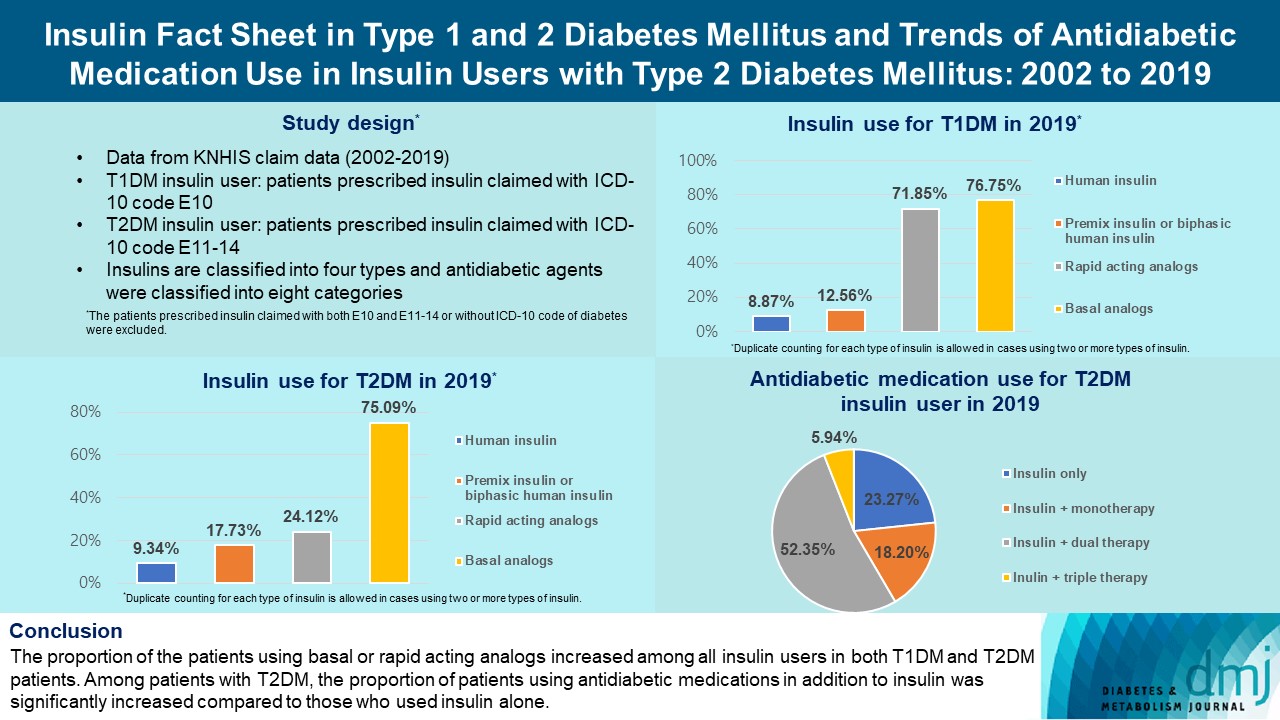
- Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
- Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):211-219. Published online February 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0346
- 3,535 View
- 258 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the trends of insulin use among Korean patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Changes in prescription of antidiabetic medications in T2DM patients taking insulin therapy were evaluated.
Methods
We analyzed data from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea to evaluate the prevalence of insulin users and trends of insulin use in T1DM and T2DM patients from January 2002 to December 2019. We also investigated numbers and types of antidiabetic medications in insulin users with T2DM.
Results
The overall total number of insulin users increased from 2002 to 2019, reaching 348,254 for T2DM and 20,287 for T1DM in 2019 compared with 109,974 for T2DM and 34,972 for T1DM in 2002. The proportion of patients using basal analogs and short acting analogs have increased and those using human insulin, premixed insulin, or biphasic human insulin have decreased (rapid acting analogs: 71.85% and 24.12% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019; basal analogs: 76.75% and 75.09% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019). The use of other antidiabetic medication in addition to insulin increased for T2DM, especially in dual therapy, reaching up to 52.35% in 2019 compared with 16.72% in 2002.
Conclusion
The proportion of the patients using basal or rapid acting analogs increased among all insulin users in both T1DM and T2DM patients. Among patients with T2DM, the proportion of patients using antidiabetic medications in addition to insulin was significantly increased compared to those who used insulin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah B. Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Review
- Technology/Device
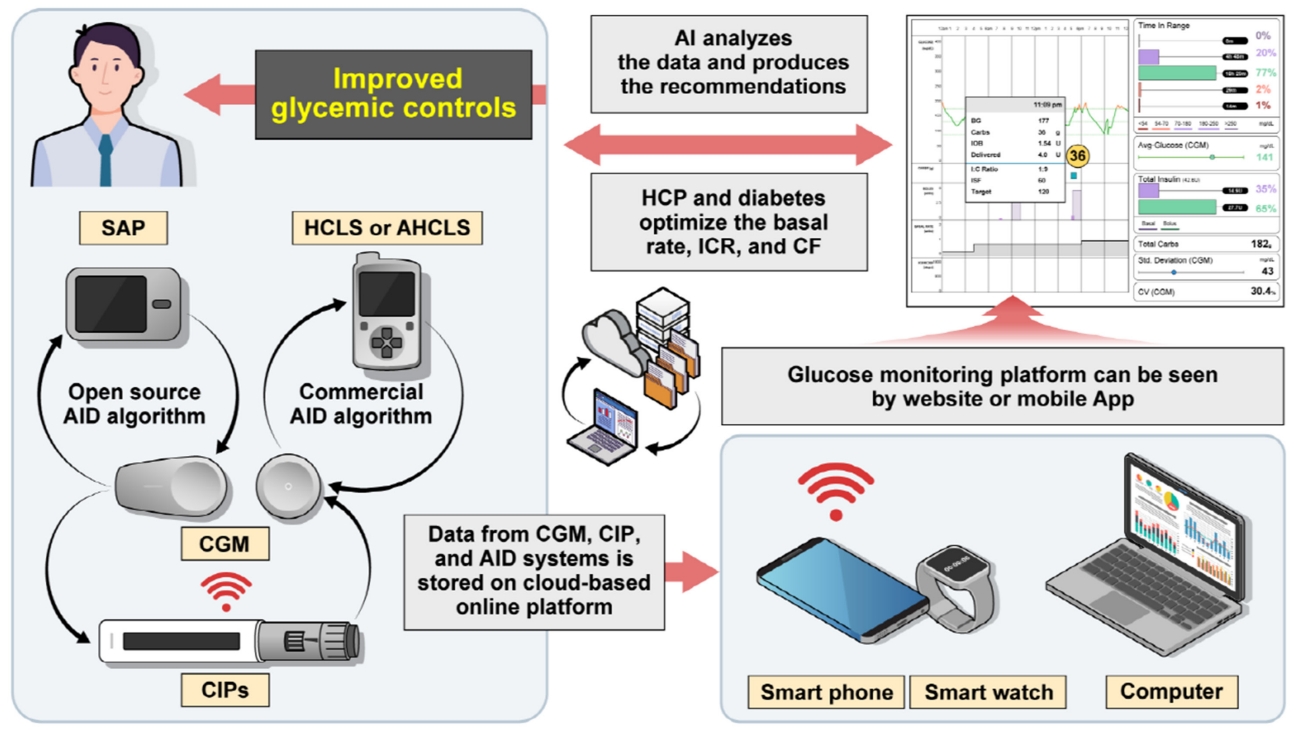
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):27-41. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0271
- 6,232 View
- 384 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology has evolved over the past decade with the integration of various devices including insulin pumps, connected insulin pens (CIPs), automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, and virtual platforms. CGM has shown consistent benefits in glycemic outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin. Moreover, the combined effect of CGM and education have been shown to improve glycemic outcomes more than CGM alone. Now a CIP is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day like insulin pumps and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator. Although only a few clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of CIPs, they consistently show benefits in glycemic outcomes by reducing missed doses of insulin and improving problematic adherence. AID systems and virtual platforms made it possible to achieve target glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes while minimizing hypoglycemia, which has always been challenging in T1DM. Now fully automatic AID systems and tools for diabetes decisions based on artificial intelligence are in development. These advances in technology could reduce the burden associated with insulin treatment for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in the precision control strategy of artificial pancreas
Wuyi Ming, Xudong Guo, Guojun Zhang, Yinxia Liu, Yongxin Wang, Hongmei Zhang, Haofang Liang, Yuan Yang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Dorothy Avoke, Abdallah Elshafeey, Robert Weinstein, Chang H. Kim, Seth S. Martin
Endocrine Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Toni L. Cordero, Zheng Dai, Arcelia Arrieta, Fang Niu, Melissa Vella, John Shin, Andrew S. Rhinehart, Jennifer McVean, Scott W. Lee, Robert H. Slover, Gregory P. Forlenza, Dorothy I. Shulman, Rodica Pop-Busui, James R. Thrasher, Mark S. Kipnes, Mark P. Ch
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(9): 652. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - APSec1.0: Innovative Security Protocol Design with Formal Security Analysis for the Artificial Pancreas System
Jiyoon Kim, Jongmin Oh, Daehyeon Son, Hoseok Kwon, Philip Virgil Astillo, Ilsun You
Sensors.2023; 23(12): 5501. CrossRef - Advances and Development of Electronic Neural Interfaces
Xue Jiaxiang, Liu Zhixin
Journal of Computing and Natural Science.2023; : 147. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Metabolic Control in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Coeliac Disease
Flavia Amaro, Maria Alessandra Saltarelli, Marina Primavera, Marina Cerruto, Stefano Tumini
Endocrines.2023; 4(3): 595. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef - Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos, Ranjit M. Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan, Charlotte Steenblock, Stefan R. Bornstein
Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic Disease.2023; 1(1): 16. CrossRef - An Observational Pilot Study of a Tailored Environmental Monitoring and Alert System for Improved Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Mohammed Alotaibi, Fady Alnajjar, Badr A Alsayed, Tareq Alhmiedat, Ashraf M Marei, Anas Bushnag, Luqman Ali
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 3799. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Original Article
- Drug/Regimen
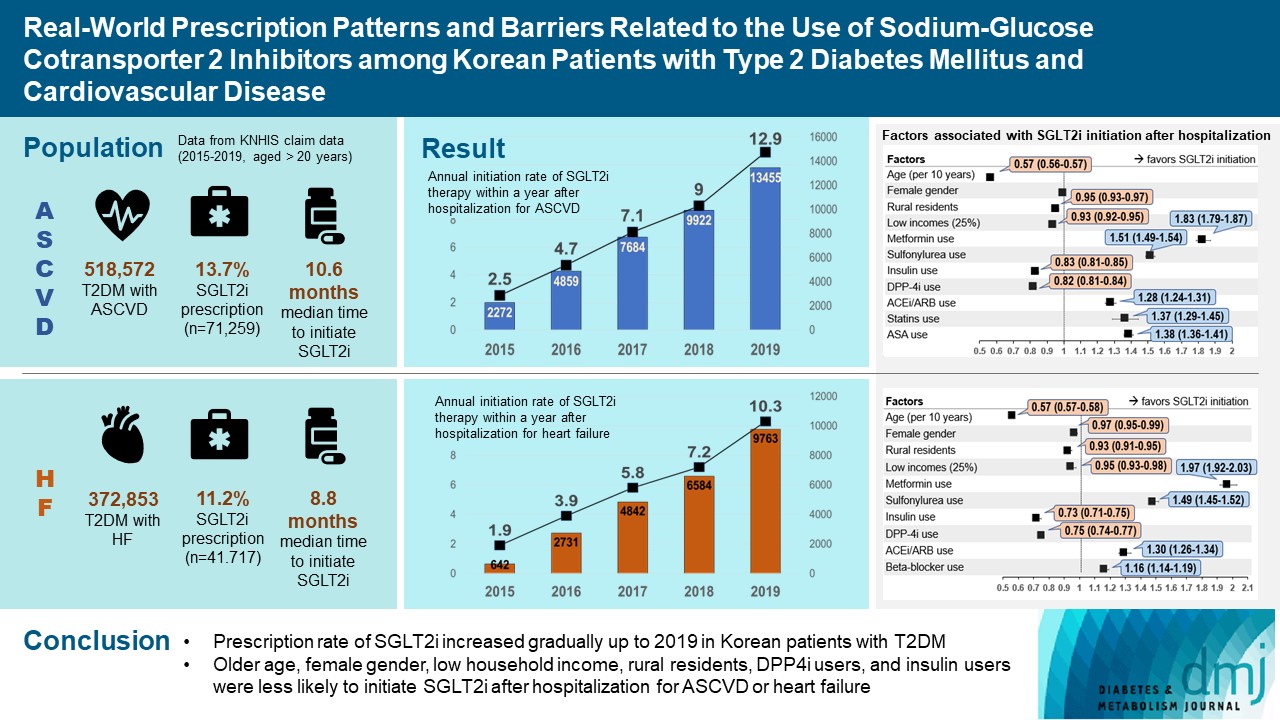
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
- Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0002
- 4,917 View
- 319 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate prescription trends and clinical factors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use according to the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heart failure (HF) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Prescription patterns of SGLT2i use between 2015 and 2019 were determined using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database of claims.
Results
Of all patients with T2DM (n=4,736,493), the annual prescription rate of SGLT2i increased every year in patients with ASCVD (from 2.2% to 10.7%) or HF (from 2.0% to 11.1%). After the first hospitalization for ASCVD (n=518,572), 13.7% (n=71,259) of patients initiated SGLT2i with a median of 10.6 months. After hospitalization for HF (n=372,853), 11.2% (n=41,717) of patients initiated SGLT2i after a median of 8.8 months. In multivariate regression for hospitalization, older age (per 10 years, odds ratio [OR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.56 to 0.57), lower household income (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.92 to 0.95), rural residents (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) users (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.84) were associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in ASCVD. Additionally, female gender (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) was associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in HF.
Conclusion
The prescription rate of SGLT2i increased gradually up to 2019 but was suboptimal in patients with ASCVD or HF. After the first hospitalization for ASCVD or HF, older age, female gender, low household income, rural residents, and DPP-4i users were less likely to initiate SGLT2i. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(3): 285. CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Hospital Readmissions for Fluid Overload among Individuals with Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Risk Factors and Multivariable Prediction Models
Jiashen Cai, Dorothy Huang, Hanis Binte Abdul Kadir, Zhihua Huang, Li Choo Ng, Andrew Ang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Yong Mong Bee, Wei Yi Tay, Chieh Suai Tan, Cynthia C. Lim
Nephron.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Prescribing patterns of SGLT-2 inhibitors for patients with heart failure: A two-center analysis
Teja Chakrala, Roshni O. Prakash, Justin Kim, Hanzhi Gao, Umar Ghaffar, Jaymin Patel, Alex Parker, Bhagwan Dass
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 28: 100286. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Short Communication
- Technology/Device
- A 4-Week, Two-Center, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of EOPatch in Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jiyun Park, Nammi Park, Sangjin Han, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Woo Je Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):941-947. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0299
- 5,168 View
- 269 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of tubeless patch pump called EOPatch in patients with well-controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). This 4-week, two-center, open-label, single-arm study enrolled 10 adult patients diagnosed with T1DM with glycosylated hemoglobin less than 7.5%. The co-primary end points were patch pump usage time for one attachment and number of serious adverse events related to the patch pump. The secondary end points were total amount of insulin injected per patch and changes in glycemic parameters including continuous glucose monitoring data compared to those at study entry. The median usage time per patch was 84.00 hours (interquartile range, 64.50 to 92.50). Serious adverse events did not occur during the trial. Four weeks later, time in range 70 to 180 mg/dL was significantly improved (70.71%±17.14 % vs. 82.96%±9.14%, P=0.01). The times spent below range (<54 mg/dL) and above range (>180 mg/dL) also improved (All P<0.05). Four-week treatment with a tubeless patch pump was safe and led to clinical improvement in glycemic control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multilayer track‐etched membrane‐based electroosmotic pump for drug delivery
Qian Yang, Zebo Zhang, Junshu Lin, Boyu Zhu, Rongying Yu, Xinru Li, Bin Su, Bo Zhao
ELECTROPHORESIS.2024; 45(5-6): 433. CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A true continuous healthcare system for type 1 diabetes
Jiyong Kim, Salman Khan, Eun Kyu Kim, Hye-Jun Kil, Bo Min Kang, Hyo Geon Lee, Jin-Woo Park, Jun Young Yoon, Woochul Kim
Nano Energy.2023; 113: 108553. CrossRef
- Multilayer track‐etched membrane‐based electroosmotic pump for drug delivery
Brief Report
- Technology/Device
- Do-It-Yourself Open Artificial Pancreas System in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data
- Min Sun Choi, Seunghyun Lee, Jiwon Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sung Min Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):154-159. Published online November 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0011
- 5,285 View
- 192 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Few studies have been conducted among Asian children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) using do-it-yourself artificial pancreas system (DIY-APS). We evaluated real-world data of pediatric T1DM patients using DIY-APS. Data were obtained for 10 patients using a DIY-APS with algorithms. We collected sensor glucose and insulin delivery data from each participant for a period of 4 weeks. Average glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.2%±0.3%. The mean percentage of time that glucose level remained in the target range of 70 to 180 mg/dL was 82.4%±7.8%. Other parameters including time above range, time below range and mean glucose were also within the recommended level, similar to previous commercial and DIY-APS studies. However, despite meeting the target range, unadjusted gaps were still observed between the median basal setting and temporary basal insulin, which should be handled by healthcare providers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Open-source automated insulin delivery systems (OS-AIDs) in a pediatric population with type 1 diabetes in a real-life setting: the AWeSoMe study group experience
Judith Nir, Marianna Rachmiel, Abigail Fraser, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener, Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, Alon Haim, Eve Stern, Noa Levek, Tal Ben-Ari, Zohar Landau
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 262. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of Android artificial pancreas system use at home among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus in China: protocol of a 26-week, free-living, randomised, open-label, two-arm, two-phase, crossover trial
Mengyun Lei, Beisi Lin, Ping Ling, Zhigu Liu, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Xubin Yang, Jing Lv, Wen Xu, Jinhua Yan
BMJ Open.2023; 13(8): e073263. CrossRef - Barriers to Uptake of Open-Source Automated Insulin Delivery Systems: Analysis of Socioeconomic Factors and Perceived Challenges of Caregivers of Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes From the OPEN Survey
Antonia Huhndt, Yanbing Chen, Shane O’Donnell, Drew Cooper, Hanne Ballhausen, Katarzyna A. Gajewska, Timothée Froment, Mandy Wäldchen, Dana M. Lewis, Klemens Raile, Timothy C. Skinner, Katarina Braune
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Toward Personalized Hemoglobin A1c Estimation for Type 2 Diabetes
Namho Kim, Da Young Lee, Wonju Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung-Min Park
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(23): 23023. CrossRef
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Original Article
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
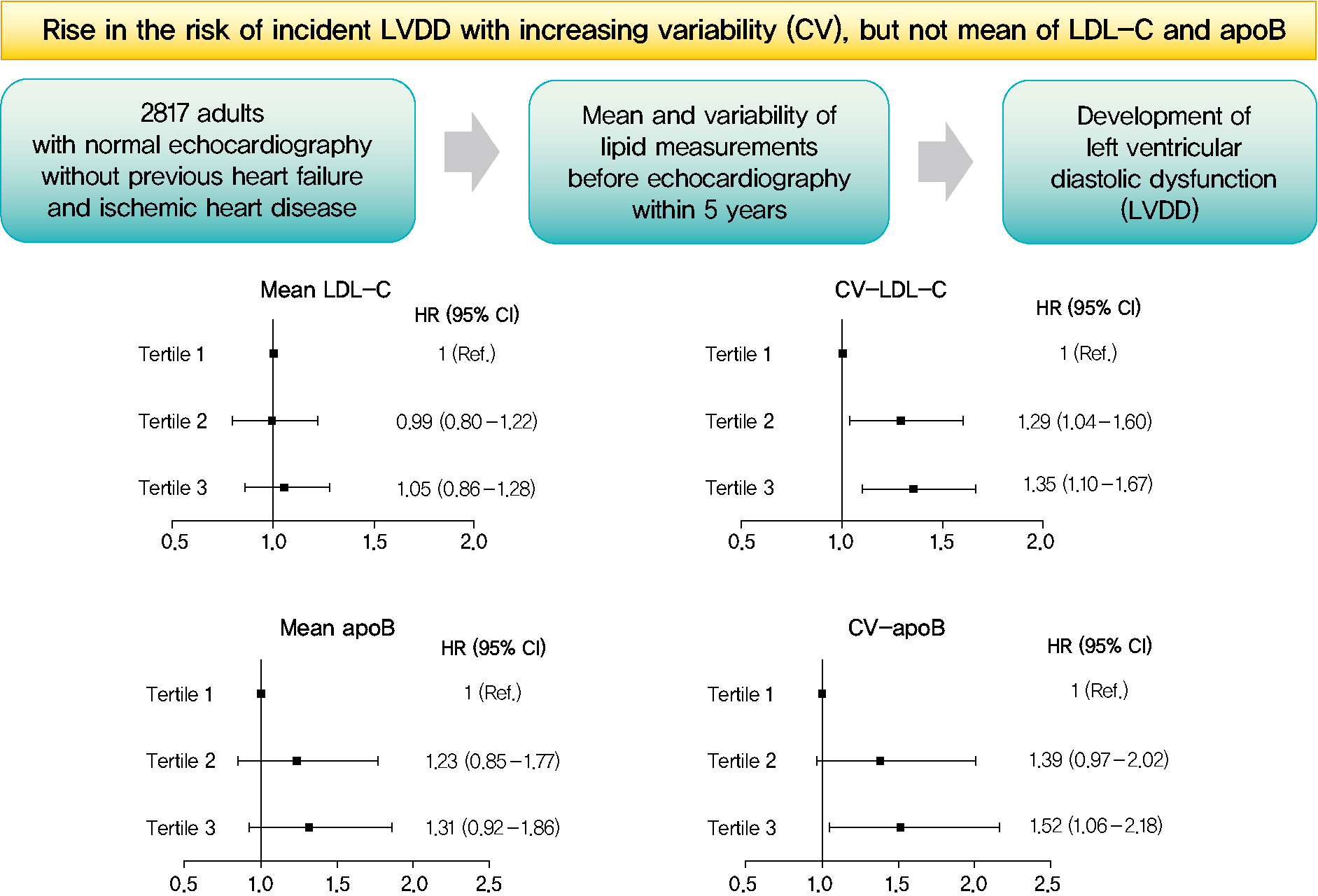
- Mean and Variability of Lipid Measurements and Risk for Development of Subclinical Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction
- Jiyun Park, Mira Kang, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Young Kim, Min Sun Choi, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Jeong Hoon Yang, Sang-Man Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):286-296. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0080
- 5,660 View
- 196 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Subclinical left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is an emerging consequence of increased insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia is one of the few correctable risk factors of LVDD. This study evaluated the role of mean and visit-to-visit variability of lipid measurements in risk of LVDD in a healthy population.
Methods
This was a 3.7-year (interquartile range, 2.1 to 4.9) longitudinal cohort study including 2,817 adults (median age 55 years) with left ventricular ejection fraction >50% who underwent an annual or biannual health screening between January 2008 and July 2016. The mean, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), variability independent of the mean (VIM), and average real variability of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apoB), non-HDL-C, and triglycerides were obtained from three to six measurements during the 5 years preceding the first echocardiogram.
Results
Among the 2,817 patients, 560 (19.9%) developed LVDD. The mean of no component of lipid measurements was associated with risk of LVDD. CV (hazard ratio [HR], 1.35; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.67), SD (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.57), and VIM (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.55) of LDL-C and all the variability parameters of apoB were significantly associated with development of LVDD. The association between CV-LDL and risk of LVDD did not have significant interaction with sex, increasing/decreasing trend at baseline, or use of stain and/or lipid-modifying agents.
Conclusion
The variability of LDL-C and apoB, rather than their mean, was associated with risk for LVDD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Jinqi Wang, Rui Jin, Xiaohan Jin, Zhiyuan Wu, Haiping Zhang, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Yueruijing Liu, Xiaoyu Zhao, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef
- Separate and Joint Associations of Remnant Cholesterol Accumulation and Variability With Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Corrigendum
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):795-795. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0256
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2020;44(6):828
- 2,920 View
- 92 Download
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Dae Jung Kim, SungWan Chun, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyun Min Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Donghyun Jee, Jae Hyun Kim, Won Seok Choi, Eun-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):461-481. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0156

- 23,950 View
- 1,626 Download
- 121 Web of Science
- 140 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) updated the previous clinical practice guidelines for Korean adults with diabetes and prediabetes and published the seventh edition in May 2021. We performed a comprehensive systematic review of recent clinical trials and evidence that could be applicable in real-world practice and suitable for the Korean population. The guideline is provided for all healthcare providers including physicians, diabetes experts, and certified diabetes educators across the country who manage patients with diabetes or the individuals at the risk of developing diabetes mellitus. The recommendations for screening diabetes and glucose-lowering agents have been revised and updated. New sections for continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pump use, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with diabetes mellitus have been added. The KDA recommends active vaccination for coronavirus disease 2019 in patients with diabetes during the pandemic. An abridgement that contains practical information for patient education and systematic management in the clinic was published separately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Subclinical Atrial Function on the Prognosis of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun-Jin Kim
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2024; 4(1): 36. CrossRef - Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Dyslipidemia and Glycated Hemoglobin in a Population-Based Study
Purum Kang, Ka Young Kim, Hye Young Shin
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 92. CrossRef - Outcomes of Various Classes of Oral Antidiabetic Drugs on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Heejoon Jang, Yeonjin Kim, Dong Hyeon Lee, Sae Kyung Joo, Bo Kyung Koo, Soo Lim, Woojoo Lee, Won Kim
JAMA Internal Medicine.2024; 184(4): 375. CrossRef - View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences
Guglielmina Froldi
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(4): 478. CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of intermittent short‐term use of a real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system in non‐insulin–treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Sun Joon Moon, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Woo Je Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Robert Vigersky, Cheol‐Young Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 110. CrossRef - Therapeutic Effects of Switching to Anagliptin from Other DPP-4 Inhibitors in T2DM Patients with Inadequate Glycemic Control: A Non-interventional, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter Observational Study
Sang-Yong Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(1): 109. CrossRef - Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Accompanied by Abdominal Obesity Additively Increases the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(5): 1173. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Justicia carnea extracts ameliorated hepatocellular damage in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic male rats via decrease in oxidative stress, inflammation and increasing other risk markers
John Adeolu Falode, Oluwaseun Igbekele Ajayi, Tolulope Victoria Isinkaye, Akinwunmi Oluwaseun Adeoye, Basiru Olaitan Ajiboye, Bartholomew I. C. Brai
Biomarkers.2023; 28(2): 177. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - The Predictive Ability of C-Peptide in Distinguishing Type 1 Diabetes From Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sajid Iqbal, Abdulrahim Abu Jayyab, Ayah Mohammad Alrashdi, Silvia Reverté-Villarroya
Endocrine Practice.2023; 29(5): 379. CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Implementation of five machine learning methods to predict the 52-week blood glucose level in patients with type 2 diabetes
Xiaomin Fu, Yuhan Wang, Ryan S. Cates, Nan Li, Jing Liu, Dianshan Ke, Jinghua Liu, Hongzhou Liu, Shuangtong Yan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Treatment Intensification by Quadruple Oral Therapy Compared to GLP-1RA Therapy in Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Real-world Data Study
Minyoung Kim, Hosu Kim, Kyong Young Kim, Soo Kyoung Kim, Junghwa Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jaehoon Jung, Jong Ha Baek
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 135. CrossRef - Safety and Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Nationwide Post-Marketing Surveillance
Jun Sung Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Jin Oh Na, Jae Hyoung Cho, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon Hee Lee, Ji-Oh Mok, Nan Hee Kim, Dong Jin Chung, Jinhong Cho, Dong Woo Lee, Sun Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 82. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Influenza vaccination trend and related factors among patients with diabetes in Korea: Analysis using a nationwide database
Dong-Hwa Lee, Bumhee Yang, Seonhye Gu, Eung-Gook Kim, Youlim Kim, Hyung Koo Kang, Yeong Hun Choe, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Seungyong Park, Hyun Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level for Primary Prevention in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 42. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 59. CrossRef - Analysis of the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes, Requirement of Insulin Treatment, and Diabetes-Related Complications among Patients with Cancer
Su Jung Lee, Chulho Kim, Hyunjae Yu, Dong-Kyu Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1094. CrossRef - The 2022 focused update of the 2018 Korean Hypertension Society Guidelines for the management of hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim, Eun Mi Lee, Shin Young Ahn, Kwang-il Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim, Ju Han Kim, Hae-Young Lee, Jang Hoon Lee, Jong-Moo Park, Eun Joo Cho, Sungha Park, Jinho Shin, Young-Kwon Kim
Clinical Hypertension.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Consistency of 1-day and 3-day average dietary intake and the relationship of dietary intake with blood glucose, hbA1c, BMI, and lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes
DaeEun Lee, Haejung Lee, Sangeun Lee, MinJin Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(1): 20. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effect of olmesartan and amlodipine on serum angiotensin-(1–7) levels and kidney and vascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension
Kyuho Kim, Ji Hye Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Soo Lim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Menopausal hormone therapy and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Health Insurance Database in South Korea–based retrospective cohort study
Jin-Sung Yuk, Jung Min Kim
Menopause.2023; 30(5): 497. CrossRef - Intensified Multifactorial Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Takayoshi Sasako, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Kohjiro Ueki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 185. CrossRef - Association between antidiabetic drugs and the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide cohort study in South Korea
Sunyoung Kim, So Young Park, Bongseong Kim, Chanyang Min, Wonyoung Cho, Dong Keon Yon, Joo Young Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 198: 110626. CrossRef - Totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in a morbidly obese patient in Korea: a case report
Ji Won Seo, Kyong-Hwa Jun
Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery.2023; 26(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of diabetes-specific oral nutritional supplements with allulose on weight and glycemic profiles in overweight or obese type 2 diabetic patients
Jihye Tak, Minkyung Bok, Hyunkyung Rho, Ju Hyun Park, Yunsook Lim, Suk Chon, Hyunjung Lim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 241. CrossRef - Associations Between Modifiable Risk Factors and Changes in Glycemic Status Among Individuals With Prediabetes
Salma Nabila, Ji-Eun Kim, Jaesung Choi, JooYong Park, Aesun Shin, Sang-Ah Lee, Jong-koo Lee, Daehee Kang, Ji-Yeob Choi
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(3): 535. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin, a novel SGLT2 inhibitor, in Korean people with type 2 diabetes: A 24‐week, multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase III trial
Soo Heon Kwak, Kyung Ah Han, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Jae Myung Yu, EunSook Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jun Goo Kang, Choon Hee Chung, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Kyu Chang Won, Sin Gon Kim, Seung Ah Cho, Bo Young Cho, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1865. CrossRef - Adjusting the Use of Glucose-Lowering Agents in the Real-World Clinical Management of People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review
Siew Pheng Chan, Lee-Ling Lim, Juliana C. N. Chan, David R. Matthews
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(5): 823. CrossRef - The association of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and kidney function in Korean adolescents using data from Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) cycle 4 (2018–2020): a cross-sectional study
Jisuk Yun, Eun-Chul Jang, Soon-Chan Kwon, Young-Sun Min, Yong-Jin Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Dapagliflozin Formate, an Ester Prodrug of Dapagliflozin, to Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate in Healthy Subjects
Hyun Chul Kim, Sangmi Lee, Siyoung Sung, Eunjin Kim, In-Jin Jang, Jae-Yong Chung
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 1203. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of monotherapy with enavogliflozin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results of a 12‐week, multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 2 trial
Ye Seul Yang, Kyung Wan Min, Seok‐O Park, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Sung Rae Cho, Kyu Chang Won, Yong Hyun Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Gwanpyo Koh, Wan Huh, Su Young Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2096. CrossRef - An Integrated Digital Health Care Platform for Diabetes Management With AI-Based Dietary Management: 48-Week Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial
You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Ji Eun Jun, Hyunjin Park, Woo Je Lee, You-Cheol Hwang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(5): 959. CrossRef - Performance of Simple Fibrosis Score in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Min Chung, Min Kyu Kang, Jun Sung Moon, Jung Gil Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of cancer incidence after pravastatin treatment
Jin Yu, Raeun Kim, Jiwon Shinn, Man Young Park, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 61. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - The era of continuous glucose monitoring and its expanded role in type 2 diabetes
Jin Yu, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Seung‐Hwan Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(7): 841. CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Asia-Pacific consensus recommendations for application of continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes management
Alice P.S. Kong, Soo Lim, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Linong Ji, Liming Chen, Yuqian Bao, Ester Yeoh, Siew-Pheng Chan, Chih-Yuan Wang, Viswanathan Mohan, Neale Cohen, Margaret J. McGill, Stephen M. Twigg
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 201: 110718. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 307. CrossRef - Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study
You-Bin Lee, Minjee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 405. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Lost in translation: assessing the nomenclature change for diabetic kidney disease in Japan
Tetsuya Babazono, Tatsumi Moriya
Diabetology International.2023; 14(4): 319. CrossRef - Effects of dapagliflozin compared with glimepiride on body composition in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: The BEYOND study
Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyoung‐Ah Kim, Kyung‐Wan Min, Tae‐Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Woo Ahn, Nan‐Hee Kim, Ie Byung Park, Ho Chan Cho, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Kang Seo Park, Seoung‐Oh Yang, Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(9): 2743. CrossRef - Topic Modeling Analysis of Diabetes-Related Health Information during the Coronavirus Disease Pandemic
Soyoon Min, Jeongwon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1871. CrossRef - Screening Test for Evaluation of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes
Ji-Oh Mok, Chan-Hee Jung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 76. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression among Korean midlife women: a cross-sectional analysis study
You Lee Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Yunmi Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibrotic Burden in the Liver Differs Across Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Subtypes
Tae Seop Lim, Ho Soo Chun, Soon Sun Kim, Ja Kyung Kim, Minjong Lee, Hyo Jung Cho, Seung Up Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(4): 610. CrossRef - Association between the number of pregnancies and cardiac target organ damages: a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korean women’s chest pain registry (KoROSE)
Hack-Lyoung Kim, Hyun-Jin Kim, Mina Kim, Sang Min Park, Hyun Ju Yoon, Young Sup Byun, Seong-Mi Park, Mi-Seung Shin, Kyung-Soon Hong, Myung-A Kim
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise therapy for diabetes mellitus
Chaiho Jeong, Tae-Seo Sohn
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 427. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Identification of individuals at risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: screening for clinically significant liver fibrosis in patients with T2DM
Tina Reinson, Ryan M Buchanan, Christopher D Byrne
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 18(5): 355. CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef - Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of stroke in adults: a meta-analysis
Min Cheol Chang, Seung Min Chung, Sang Gyu Kwak
Reviews on Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Incident infection risks depending on oral antidiabetic exposure in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes patients
Sanghwa Park, Jiseon Jeong, Yunna Woo, Yeo Jin Choi, Sooyoung Shin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(3): 237. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review
Wah-Kheong Chan, Kee-Huat Chuah, Ruveena Bhavani Rajaram, Lee-Ling Lim, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene Ratna Vethakkan
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(3): 197. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 632. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Riesgo residual. Conclusiones
Ángel Cequier, José Luis Zamorano
Revista Española de Cardiología Suplementos.2023; 23: 25. CrossRef - Intake of Fruit and Glycemic Control in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunju Yoon, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 538. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coleus forskohlii Root Extract (ForcslimTM) as a Prospective Antidiabetic Agent: In vitro Glucose Uptake Stimulation and α-Amylase Inhibitory Effects
Firoz Hirehal Hussain Mi, Channangihalli Thimmegowda Sadashiva, Neethumol Benny, Sreedrisya Ayippakkari Kuttiattu, Ravi Subban
International Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 19(5): 730. CrossRef - Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 837. CrossRef - Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 846. CrossRef - Strategies to Maintain the Remission of Diabetes Following Metabolic Surgery
Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2023; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - East Asian perspectives in metabolic and bariatric surgery
Tae Jung Oh, Hyuk‐Joon Lee, Young Min Cho
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 756. CrossRef - Recent Updates to Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus
Jin Yu, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 26. CrossRef - Association between Physical Exercise and Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Korean Patients Diagnosed with Diabetes
Il Yun, Hye Jin Joo, Yu Shin Park, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3280. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of teneligliptin added to patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by oral triple combination therapy: A multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, and placebo‐controlled study
Minyoung Lee, Woo‐je Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(6): 1105. CrossRef - Trends of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(8): 1438. CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Cardiorenal Risk Profiles Among Data-Driven Type 2 Diabetes Sub-Phenotypes: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the China Health and Nutrition Survey
Hui Gao, Kan Wang, Wensui Zhao, Jianlin Zhuang, Yu Jiang, Lei Zhang, Qingping Liu, Fariba Ahmadizar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Individualized Medical Nutrition Therapy for Diabetic Patients according to Diabetes Medication
Juyeon Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 50. CrossRef - Critical shear stress of red blood cells as a novel integrated biomarker for screening chronic kidney diseases in cases of type 2 diabetes
Il Rae Park, Jimi Choi, Eun Young Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Sehyun Shin, Sin Gon Kim, Kyu Chang Won
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2022; 81(4): 293. CrossRef - Effects of exercise on reducing diabetes risk in Korean women according to menopausal status
Jung-Hwan Cho, Hye-Mi Kwon, Se-Eun Park, Ju-Hwan Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 75. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Free Versus Fixed-Ratio Combination of Basal Insulin and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Systematic Review and Indirect Treatment Comparison
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Se Hee Min, Hwi Seung Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Chang Hee Jung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia in Korean adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a special report of the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ga Bin Lee, Yoonjung Kim, Suyeon Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Kyungwon Oh
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022041. CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 417. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Effect of Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets and Intermittent Fasting on Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension Management: Consensus Statement of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 355. CrossRef - Effect of carbohydrate-restricted diets and intermittent fasting on obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension management: consensus statement of the Korean Society for the Study of obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Clinical Hypertension.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Personalized Diabetes Self-care Using an Electronic Medical Record–Integrated Mobile App in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: 6-Month Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Young Lee, Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Min Kyung Hyun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(7): e37430. CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Tolerability and Effectiveness of Switching to Dulaglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled With Insulin Therapy
Youngsook Kim, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Utilization of Diabetes Complication Tests Under the COVID-19 Pandemic: Machine Learning Approach
Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of prediabetes with death and diabetic complications in older adults: the pros and cons of active screening for prediabetes
Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Hyun Ho Choi, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Age and Ageing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent information on test utilization and intraindividual change in anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody in Korea: a retrospective study
Rihwa Choi, Wonseo Park, Gayoung Chun, Jiwon Lee, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(3): e002739. CrossRef - Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 415. CrossRef - Pharmacological Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Antidiabetic Agents
Kyung-Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(2): 83. CrossRef - Maintaining Physical Activity Is Associated with Reduced Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in People Newly Diagnosed with Diabetes
Duhoe Kim, Jaehun Seo, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 187. CrossRef - Effect of Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets and Intermittent Fasting on Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension Management: Consensus Statement of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, Korean Diabetes Association, and Korean Society of Hype
Jong Han Choi, Yoon Jeong Cho, Hyun-Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Suk Chon, Jee-Hyun Kang, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Eun Mi Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Ga Eun Nam, Kwang Il Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 100. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Current status of obesity treatment in Korea: based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 388. CrossRef - Experiences of Using Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitors in Adults With Diabetes: A Qualitative Descriptive Study
Hee Sun Kang, Hyang Rang Park, Chun-Ja Kim, Savitri Singh-Carlson
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2022; 48(5): 362. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Association of underweight status with the risk of tuberculosis: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Su Hwan Cho, Hyun Lee, Hyuktae Kwon, Dong Wook Shin, Hee-Kyung Joh, Kyungdo Han, Jin Ho Park, Belong Cho
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the risk factors of impaired fasting glucose in middle-aged population living in South Korean communities by using categorical boosting machine
Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - External validation and clinical application of the predictive model for severe hypoglycemia
Jae-Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Soo-Yeon Choi, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Euonymus alatus Extracts on Diabetes Related Markers in Pancreatic β-Cells and C57BL/Ksj-db/db Mice
Ye Rin Kim, Eun-young Kim, Seong Uk Lee, Young Wan Kim, Yoon Hee Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 51(9): 894. CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Correlation between shift work and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among male workers in the steel manufacturing company of Korea: a cross-sectional study
Kiseok Kim, Yong-Jin Lee, Soon-Chan Kwon, Young-Sun Min, Hyun Kyo Lee, Gwangin Baek, Sang Hyeon Kim, Eun-Chul Jang
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - FGM-based remote intervention for adults with type 1 diabetes: The FRIEND randomized clinical trial
Jinju Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Jiyun Park, Kyung-Soo Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Hyun Wook Han, Young Shin Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Control in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yaeni Kim, Won Kim, Jwa-Kyung Kim, Ju Young Moon, Samel Park, Cheol Whee Park, Hoon Suk Park, Sang Heon Song, Tae-Hyun Yoo, So-Young Lee, Eun Young Lee, Jeonghwan Lee, Kyubok Jin, Dae Ryong Cha, Jin Joo Cha, Sang Youb Han
Electrolytes & Blood Pressure.2022; 20(2): 39. CrossRef - The Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study: Methods and Initial Baseline Data
Yoon Jeong Cho, Sohyun Park, Sung Soo Kim, Hyo Jin Park, Jang Won Son, Tae Kyung Lee, Sangmo Hong, Jee-Hyun Kang, Seon Mee Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won Jun Kim, Young Eun Seo, Yoosuk An, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sookyoung Jeon, Kyungho Park, Bong-Soo Kim, Cha
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 303. CrossRef - Oral Semaglutide, the First Ingestible Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist: Could It Be a Magic Bullet for Type 2 Diabetes?
Hwi Seung Kim, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 9936. CrossRef - Long-term effectiveness and safety of quadruple combination therapy with empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 3-year prospective observational study
Eu Jeong Ku, Dong-Hwa Lee, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Tae Keun Oh
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 182: 109123. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:698-707)
Mi-kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 968. CrossRef - Incidence and Risk Factors for Progression to Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Min Kyung Hyun, Jong Heon Park, Kyoung Hoon Kim, Soon-Ki Ahn, Seon Mi Ji
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 123. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Pharmacotherapy and the Korean Diabetes Association Support System
Kyu Yeon Hur
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 250. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 259. CrossRef
- Impact of Subclinical Atrial Function on the Prognosis of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Metabolic Syndrome
Original Article
- Drug/Regimen
- Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
- Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):81-92. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0016
- 7,555 View
- 431 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the effects of teneligliptin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-derived time in range, and glycemic variability in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in eight centers in Korea (clinical trial registration number: NCT03508323). Sixty-five participants aged ≥65 years, who were treatment-naïve or had been treated with stable doses of metformin, were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive 20 mg of teneligliptin (n=35) or placebo (n=30) for 12 weeks. The main endpoints were the changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 12, CGM metrics-derived time in range, and glycemic variability.
Results
After 12 weeks, a significant reduction (by 0.84%) in HbA1c levels was observed in the teneligliptin group compared to that in the placebo group (by 0.08%), with a between-group least squares mean difference of –0.76% (95% confidence interval [CI], –1.08 to –0.44). The coefficient of variation, standard deviation, and mean amplitude of glycemic excursion significantly decreased in participants treated with teneligliptin as compared to those in the placebo group. Teneligliptin treatment significantly decreased the time spent above 180 or 250 mg/dL, respectively, without increasing the time spent below 70 mg/dL. The mean percentage of time for which glucose levels remained in the 70 to 180 mg/dL time in range (TIR70–180) at week 12 was 82.0%±16.0% in the teneligliptin group, and placebo-adjusted change in TIR70–180 from baseline was 13.3% (95% CI, 6.0 to 20.6).
Conclusion
Teneligliptin effectively reduced HbA1c levels, time spent above the target range, and glycemic variability, without increasing hypoglycemia in our study population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Harmanjit Singh, Ravi Rohilla, Shivani Jaswal, Mandeep Singla
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 81. CrossRef - Potential approaches using teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: current status and future prospects
Harmanjit Singh, Jasbir Singh, Ravneet Kaur Bhangu, Mandeep Singla, Jagjit Singh, Farideh Javid
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Mechanism of molecular interaction of sitagliptin with human DPP4 enzyme - New Insights
Michelangelo Bauwelz Gonzatti, José Edvar Monteiro Júnior, Antônio José Rocha, Jonathas Sales de Oliveira, Antônio José de Jesus Evangelista, Fátima Morgana Pio Fonseca, Vânia Marilande Ceccatto, Ariclécio Cunha de Oliveira, José Ednésio da Cruz Freire
Advances in Medical Sciences.2023; 68(2): 402. CrossRef - A prospective multicentre open label study to assess effect of Teneligliptin on glycemic control through parameters of time in range (TIR) Metric using continuous glucose monitoring (TOP-TIR study)
Banshi Saboo, Suhas Erande, A.G. Unnikrishnan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(2): 102394. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef
- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





